Network Harmony: The Art of Ethernet Switching
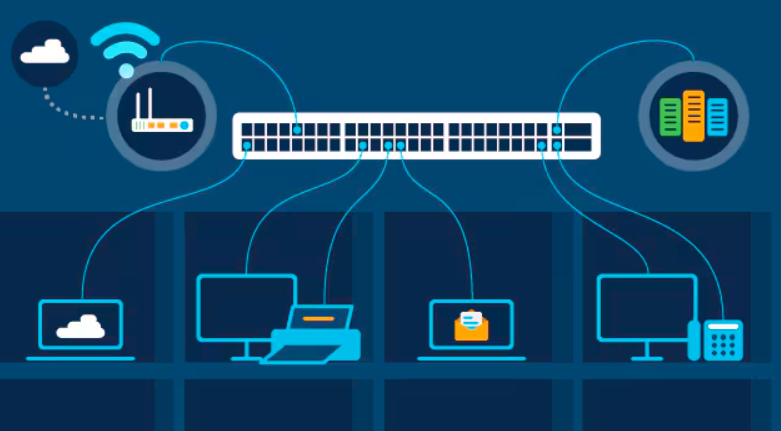
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Ethernet Switching
- How Ethernet Switches Work
- Types of Ethernet Switches
- Benefits of Ethernet Switching
- Everyday Use Cases for Ethernet Switching
- Best Practices for Implementing Ethernet Switching
- Challenges and Considerations
- The Future of Ethernet Switching
Introduction to Ethernet Switching
Ethernet switching is foundational in network design, allowing for effective data handling across local area networks (LANs). By creating a dedicated path for data packets, switches prevent data collisions and reduce congestion, thus enhancing network performance. With data flows becoming increasingly intricate, understanding Ethernet switches becomes crucial to managing network traffic efficiently. You can explore Ethernet switches in Fortinet’s glossary to grasp their pivotal role in facilitating smooth data transmission across devices. Understanding this technology is vital as networks become more sophisticated, requiring precise data management strategies to maintain efficiency. This foundational technology has evolved to tackle the growing complexity of contemporary digital environments, making its study timely and necessary for anyone involved in network design or administration.
How Ethernet Switches Work
At their core, Ethernet switches utilize network protocols to forward data between devices. They examine data packets’ source and destination MAC addresses, deciding the best path within the network for each packet. This process is akin to how a skilled traffic officer directs vehicles at a busy intersection, ensuring that each car—or data packet—reaches its designated destination promptly and safely. By creating a series of interconnected pathways, switches effectively transform a chaotic flow of information into a symphonious network environment.
Types of Ethernet Switches
Ethernet switches come in various forms, each designed to meet specific network needs. From basic models suitable for home use to advanced ones for large corporations, understanding the different types can help you select the best switch for your network.
- Unmanaged Switches: Unmanaged switches are the simplest option, perfect for users who need a straightforward setup. These switches are typically plug-and-play, requiring no configurations. They’re excellent for basic networking tasks, such as connecting devices in a small office or home network. Without the need for complex adjustments, unmanaged switches provide reliable service for environments where simplicity trumps configurability, making them a popular choice for those with modest networking demands.
- Managed Switches: Managed switches offer various configurability options that allow network administrators to tailor traffic management to the organization’s needs. Features like VLANs, SNMP, and QoS grant administrators detailed control over the network, enabling them to allocate resources dynamically, monitor network health, and ensure quality of service across all connected devices. These capabilities make managed switches indispensable for more extensive or mixed-use networks where high performance and security are paramount. Real-time adjustments and monitoring ensure that the network remains agile and can handle the dynamic demands of modern workflows.
- Smart Switches: Smart switches fill the gap between unmanaged and fully managed switches, offering limited configurability without the complexity of complete management. They are suitable for small to medium-sized businesses that need more than a simple plug-and-play solution but do not require comprehensive management features. These switches offer a practical balance, providing network optimization options while maintaining ease of use, making them versatile additions to networks in transition or growth phases.
Benefits of Ethernet Switching
Using Ethernet switches carries several advantages, from enhancing network scalability to improving overall performance. By isolating collision domains, switches reduce traffic congestion, allowing faster data transmission. Moreover, their ability to prioritize traffic ensures that critical data is delivered without delay, which is crucial for applications requiring high reliability and speed. Managing data flows flexibly renders Ethernet switches essential to establishing a high-performance network architecture that supports future expansion and technological progress.
Everyday Use Cases for Ethernet Switching
Ethernet switching is employed across various domains due to its adaptability. In corporate environments, it manages extensive device connections and high data traffic, whereas, in smaller settings like homes or small offices, it ensures all devices can access the network reliably. Data centers rely on Ethernet switches to manage server workloads and backup systems, maintaining constant uptime and high-speed data processing. This wide range of applications demonstrates the versatility and reliability of Ethernet switches, accommodating the unique challenges and demands of differing environments.
Read also: What role does technology play in education reform in the USA?
Best Practices for Implementing Ethernet Switching
Implementing Ethernet switching requires thoughtful planning and a strategic approach. First, understand your network’s scale and requirements to choose the right types of switches. Network mapping should be employed to visualize current and future infrastructure needs, aiding in strategic deployments. Regularly update switch firmware to protect against vulnerabilities and keep the network running smoothly. Additionally, redundancy and backup systems should be incorporated to prevent disruptions, ensuring the network remains resilient against unforeseen failures or overloads. Following these best practices will ensure your network meets current demands and is prepared for future growth.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their many advantages, Ethernet switches also present challenges. Incompatibility issues between devices and switches can lead to network inefficiencies, requiring careful attention during setup. Network hardware maintenance is another consideration, as neglected switches can become bottlenecks, impacting performance. Furthermore, planning for future scalability is crucial to avoid outgrowing network capabilities, which can involve significant reconfigurations or upgrades if not addressed proactively. Balancing these factors is essential for maintaining a high-performance, reliable, and adaptable network architecture.
The Future of Ethernet Switching
The future of Ethernet switching is poised to evolve with emerging technological trends. As innovations like IoT and 5G expand, Ethernet switching adapts to meet new data demands, integrating with these technologies to offer higher speeds and enhanced connectivity. The switching landscape is also expected to see advancements in energy efficiency and intelligent management, making networks more sustainable and easier to control. Embracing these future developments ensures that networks remain at the forefront of technological capability and efficiency. For further insights, the future of network hardware holds exciting prospects and pivotal trends worth exploring.